What is the Role of VoIP Codecs in the Call Audio Quality?

Outperforming PSTN services with its myriad of features and benefits, A-Z VoIP termination services have become a destination for business communication needs for many companies especially in the IT domain - both big and small across the world. A user is confined to phone communications when using the PSTN but with VoIP, one can receive and make calls on desk phones, softphones (cloud-based software), and smartphone devices that run on Apple iOS, Windows Phone, and Google Android. This makes communication smoother, and there are numerous systems that enable seamless switching between VoIP endpoints.
The VoIP technology is built in such a way that it can convert your data, voice, or video calls into digital signals and as a result delivers clear communication, without the use of huge, expensive, and complex telecommunications equipment. It converts auditory information into data packets, bypassing the typical PSTN data transfer.
Despite being aware of the benefits, switching to VoIP is still a path of concern and resistance for many businesses. Changing or upgrading to new technology can be intimidating as businesses fear untapped loopholes and find it easier to stick to the traditional and known territory when it comes to technology.
A company that wishes to switch to VoIP can simply buy hosted services and start using them for all their business communication needs. However, understanding the underlying technology, protocols, and how VoIP works is required to unlock advanced capabilities and the full potential of VoIP. Let’s discuss how VoIP delivers voice quality and uses internet bandwidth to transmit the data and facilitate business conversations.
To get an insight into how it works, we need to first understand VoIP Codecs. Codecs are responsible for faster download of a movie, data encryption, streaming media on Netflix or similar platforms. It is codecs that determine the bandwidth and the quality of files you access.
What Role do Codecs Play in Wholesale VoIP Services?
VoIP codec is responsible for converting analog voice signals into digital packets for efficient transmission and again converting them back into uncompressed audio signals. Through VoIP codecs, one can determine the latency and audio quality while placing the call over the internet.
There are a number of options to choose from in VoIP codecs. These codecs can be primarily differentiated on the way each codec compresses audio and having some key information on them can help you optimize your VoIP services.
Here are 4 Commonly Used VoIP Codecs and their features.
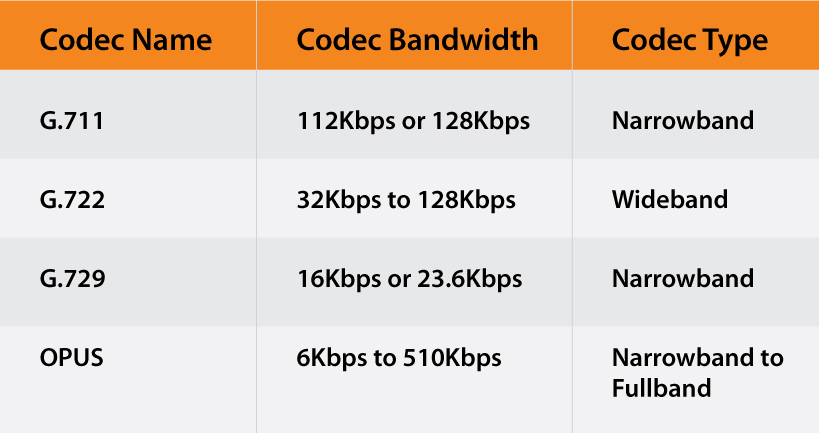
G.711 Codecs
The G.711 VoIP codec is known to provide excellent sound quality, but it demands the most bandwidth as compared to other codecs. To use this codec, one requires at least 96Kbps per line of bandwidth. You can use this codec with less compression if audio quality is your priority. However, that will necessitate a bandwidth of 112Kbps or 128Kbps per line.
If you require high-definition audio quality, this codec is a solid alternative. Because the G.711 codec does not use digital compression, it's also an excellent choice if your VoIP system involves connecting to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
G.722 Codecs
One of the most adaptable VoIP codecs is the G.722. This codec only requires 32Kbps per line at its greatest compression rate. One can utilize up to 128Kbps per line if more bandwidth is available and better audio quality is needed. This codec is ideal even when one wants to temporarily increase compression to add more VoIP lines while maintaining the same amount of bandwidth.
G.729 Codecs
The G.729 VoIP codec needs the least amount of bandwidth with just 12.8Kbps per line at its greatest compression rate. This codec generally requires 16Kbps or 23.6Kbps per line.
The codec's audio quality is exceptional considering its minimal bandwidth needs. If connecting numerous VoIP lines is a priority for a business, G.729 is a suitable fit. Its minimal bandwidth allows one to make the most of the internet connection.
OPUS
OPUS is considered the most reliable VoIP codec for sending high-quality audio over the internet by employing cutting-edge compression techniques.
Easy to adapt, the OPUS codec can be used to produce high-quality audio and crystal-clear speech as it can handle bitrates ranging from 6 to 510 kbps and sampling rates from 8 to 48 kHz.
This codec was created for Web Real-Time Communication, but as their SIP phones demonstrate, it is no longer compatible with browser-based telephony. OPUS codes also support voice recording and wireless audio. It handles low latency concerns effectively; however lossless audio compression of the codec still has scope for improvement.
Choose a Codec that Caters to Your A-Z VoIP Termination Service Needs
When deciding which codec to deploy for A-Z VoIP termination services at an organization, one must remember that codecs are basically data compressor and decompressor. They compress the data in order to send it over the available bandwidth briskly, while a codec on the receiving end decompresses it to make it useful again. Small chunks of data are frequently lost throughout this process. Voice calls can become distorted if the chosen codec discards too much audio. Such difficulties can have a significant detrimental impact on corporate contacts, especially during negotiations or customer service calls.
Thus, to experience flawless, jitter-free voice audio quality while conversing with clients, a business must choose a codec that caters to its needs and as a result, avert most bandwidth challenges and issues with the audio transmitted, such as quality, latency, and echo.
Harshita Kapoor
Harshita is a Content Writer at Panamax. Inc. MBA in HR & Marketing, she found her calling in Content Writing. In a short span of 2 years, she has explored writing in different styles of content like Coffee table books, website content and for media. In her time of leisure, she finds happiness in binge watching classics & practicing yoga.

 Fostering Authentic Connections: The Power of P2P SMS-Enabled Numbers and DID Services in Customer Engagement
Fostering Authentic Connections: The Power of P2P SMS-Enabled Numbers and DID Services in Customer Engagement